Create an Atlas Search Index
On this page
You can create an Atlas Search index through the Atlas UI, API, and Atlas CLI.
Prerequisites
To create an Atlas Search index, you must have an Atlas cluster with:
- MongoDB version
4.2or higher - Collection to create the Atlas Search index for
The following table shows the modes of access each role supports.
Role | Action | Atlas UI | Atlas API | Atlas Search API | Atlas CLI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Project Data Access Read Only or higher role | To view Atlas Search analyzers and indexes. | ✓ | ✓ | ||
Project Data Access Admin or higher role | To create and manage Atlas Search analyzers and indexes, and
assign the role to your API Key. | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Project Owner role | ✓ | ✓ | |||
Organization Owner role | To create access list entries for
your API Key and send the request from a client that appears in the
access list for your API Key. | ✓ | ✓ | ||
To create, view, edit, and delete Atlas Search indexes using the
Atlas UI or API. | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Create an Atlas Search Index Using the Atlas UI
When you create a new Atlas Search index, choose a configuration method.
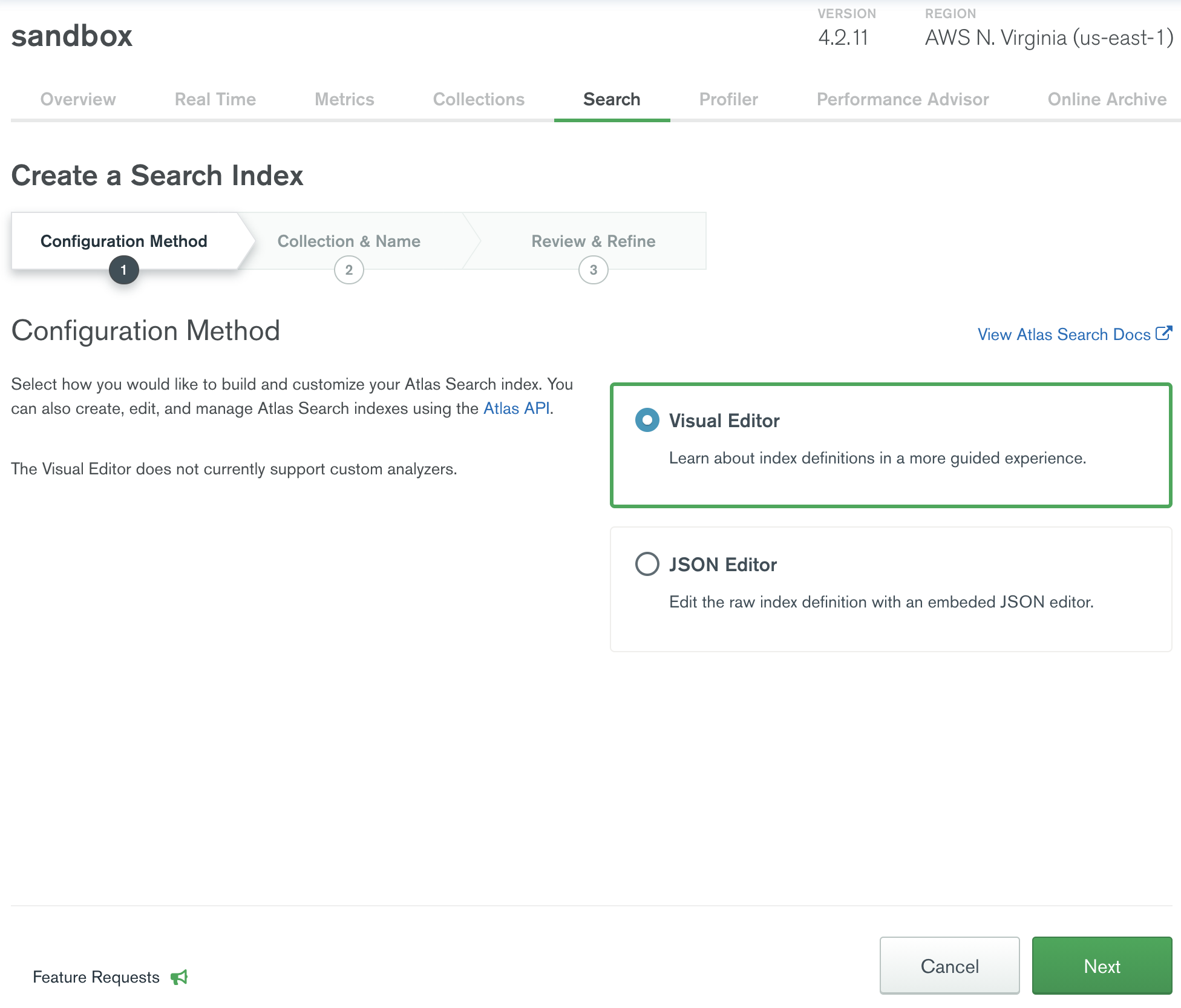
You can use either the default index definition or specify a custom definition for the index. The default index definition is dynamic mapping of fields in the documents and will work with any collection. If you wish to create a custom index definition for static mapping, you can specify which fields to index with which analyzer and as which data type.
The index name defaults to default. You can leave the default name in place or choose one of your own.
If you name your index default, you don't need to specify
an index parameter when using the $search pipeline stage. Otherwise, you must specify
the index name using the index parameter.
Index names must be unique within their namespace.
To create an Atlas Search index from the Atlas UI:
Select a Configuration Method and click Next.
For a guided experience, select Visual Editor.
NoteThe Visual Editor doesn't support custom analyzers or synonym mapping definitions.
- To edit the raw index definition, select JSON Editor.
Enter the Index Name, and set the Database and Collection.
In the Index Name field, enter a name for the index.
NoteIf you name your index
default, you don't need to specify anindexparameter when using the $search pipeline stage. Otherwise, you must specify the index name using theindexparameter.- In the Database and Collection section, find the database or collection, and select the collection name.
- If you use the Visual Editor, click Next.
Customize your Atlas Search index configuration settings.
If you are using the Visual Editor, click Refine Your Index to make changes to any of the following settings and click Save Changes.
Field NameDescriptionNecessityIndex AnalyzerOptionalSearch AnalyzerOptionalDynamic MappingSpecify dynamic or static mapping of fields. To disable dynamic mapping, set
"dynamic":toOff. By default, dynamic mapping is enabled. If you disable dynamic mapping, you must specify the fields to index. To learn more about dynamic and static mappings, see Review Atlas Search Index Syntax.Corresponds to the
mappings.dynamicsetting.RequiredStore Full DocumentNoteThe Atlas Search index storedSource option and
$searchreturnStoredSource option are in preview, but can be used in production applications. If there are any syntax or behavior changes between the preview stage and general availability (GA), we will proactively communicate before introducing any breaking changes. The MongoDB Cloud Support team will help troubleshoot any issues related to using this feature as part of your contract.Specify whether to store entire documents on Atlas Search for query-time lookups. If this is enabled, Atlas Search stores all the fields in the documents by default. You can exclude specific fields from storage on Atlas Search in the Field Mappings definition for the fields. To learn more about storing fields, see Define Stored Source Fields in Your Atlas Search Index.
RequiredField MappingsRequired if dynamic mapping is disabled.
To add the fields to index, you must specify the following settings for each field:
- Field name - Name of the field to index.
- Enable Dynamic Mapping - Static or dynamic mapping to use. If you disable dynamic mapping, the data in the field isn't automatically indexed.
Store Original Value - Flag to store field on Atlas Search for query-time lookups. This is enabled by default if Store Full Document is enabled. However, you can toggle the setting to Off to exclude the field from storage. To learn more about storing fields, see Define Stored Source Fields in Your Atlas Search Index.
NoteThe Atlas Search index storedSource option and
$searchreturnStoredSource option are in preview, but can be used in production applications. If there are any syntax or behavior changes between the preview stage and general availability (GA), we will proactively communicate before introducing any breaking changes. The MongoDB Cloud Support team will help troubleshoot any issues related to using this feature as part of your contract.- Data Type Configuration - Field data type. To learn more about the supported data types and their options, see BSON Data Types and Atlas Search Field Types.
NoteUnlike compound indexes, the order of fields in the Atlas Search index definition is not important. Fields can be defined in any order.
Corresponds to the
mappings.fieldssetting.ConditionalIf you are using the JSON Editor, replace the default definition with any of the following settings and click Next. To learn more about index definition settings, see Review Atlas Search Index Syntax.
Field NameDescriptionNecessityanalyzerOptionalsearchAnalyzerOptionalmappings.dynamicSpecify dynamic or static mapping of fields. To disable dynamic mapping, set
"dynamic":tofalse. By default, dynamic mapping is enabled. If you disable dynamic mapping, you must specify the fields to index. To learn more about dynamic and static mappings, see Review Atlas Search Index Syntax.Requiredmappings.fieldsRequired if dynamic mapping is disabled.
Specify the fields that you would like to index. To learn more, see Define Field Mappings.
NoteUnlike compound indexes, the order of fields in the Atlas Search index definition is not important. Fields can be defined in any order.
ConditionalstoredSourceNotestoredSourceis only available on Atlas clusters running one of the following versions:- MongoDB 4.4.12+
- MongoDB 5.0.6+
Specify fields in the documents to store for query-time look-ups using the returnedStoredSource option. Value can be one of the following:
true, to store all fieldsfalse, to not store any fields- Object that specifies the
fields to
includeorexcludefrom storage
If omitted, defaults to
false. To learn more about the syntax and fields, see Define Stored Source Fields in Your Atlas Search Index.NoteYou can store fields of all BSON Data Types on Atlas Search.
OptionalsynonymsSpecify synonym mappings to use in your index. To learn more, see Define Synonym Mappings in Your Atlas Search Index.Optional
Optional: If you use the Visual Editor, you can save or delete your index definition draft.
If you use the Visual Editor and your index definition contains static mappings, you can save an index definition as a draft. You can't save the default index definition as a draft. You can save only a custom index definition as a draft.
- Click Cancel.
- Click Save Draft or Delete Draft.
You can't create a new index when you have a pending index draft.
To learn more about creating an index using an index draft, see Resume or Delete an Atlas Search Index Draft.
Check the status.
The newly created index appears on the Search tab. While the index is building, the Status field reads Build in Progress. When the index is finished building, the Status field reads Active.
Larger collections take longer to index. You will receive an email notification when your index is finished building.
Create an Atlas Search Index Using the Atlas Search API
To create an Atlas Search index, send a POST request to the
fts/indexes endpoint. To learn more about the
syntax and parameters for this endpoint, see
Create an Atlas Search Index.
Atlas doesn't create the index if the collection doesn't exist,
but it still returns a 200 status.
Create an Atlas Search Index Using the Atlas CLI
To create an Atlas Search index:
Run the atlas clusters search indexes create
command. To learn more about the syntax and options for the
command, see atlas clusters search indexes create.
Node Status
When you create the Atlas Search index, the Atlas Search Indexes tab in the right-side panel of the Atlas UI displays information about Atlas Search indexes for the selected namespace. The Status column shows the current state of the index on the primary node of the cluster. Click the View status details link below the status to view the state of the index on all the nodes of the cluster.
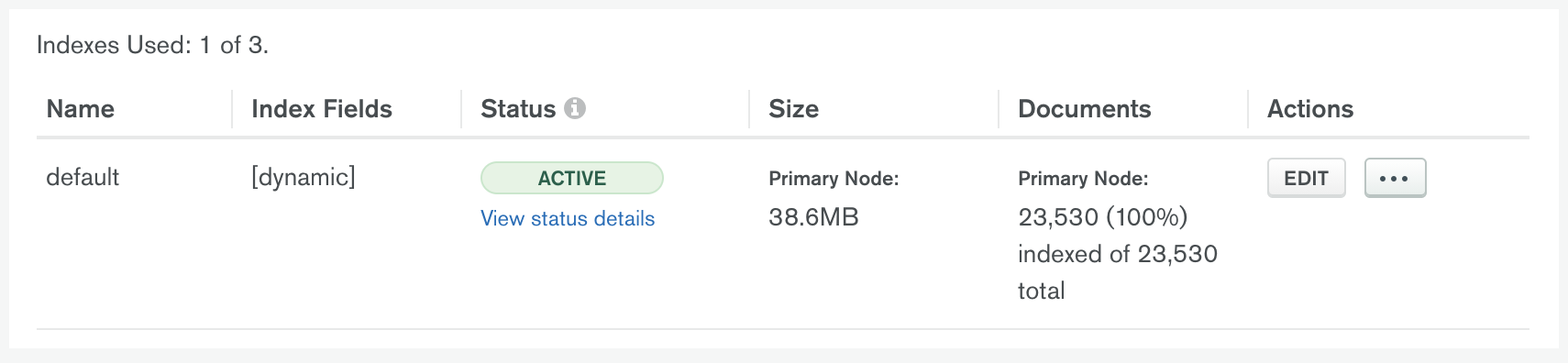
When the Status column reads Active, the index is ready to use. In other states, queries against the index may return incomplete results.
Status | Description |
|---|---|
Not Started | Atlas has not yet started building the index. |
Initial Sync | Atlas is building the index or re-building the
index after an edit. In this state, Atlas Search does not serve queries. |
Active | Index is ready to use. |
Recovering | Replication encountered an error. This state commonly occurs
when the current replication point is no longer available on the
mongod oplog. You can still query the existing index until it
updates and its status changes to Active. Use the
error in the View status details modal window to
troubleshoot the issue. To learn more, see
Fix Atlas Search Issues. |
Failed | Atlas could not build the index. Use the error
in the View status details modal window to
troubleshoot the issue. To learn more, see
Fix Atlas Search Issues. |
Delete in Progress | Atlas is deleting the index from the cluster nodes. |
While Atlas builds the index and after the build completes, the Documents column shows the percentage and number of documents indexed. The column also shows the total number of documents in the collection.